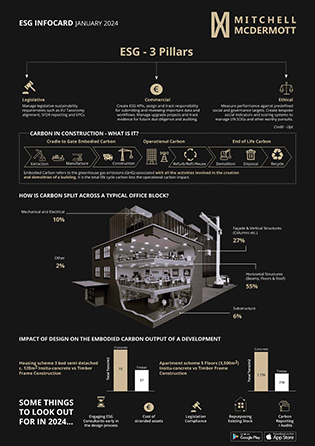
Industrial & Logistics – Irish Market Report 2024
Introduction
The Irish industrial and logistics sector is experiencing robust demand driven by certain factors such as undersupply, low vacancy rates, and fewer new sites starting construction. The market is adapting with a shift towards suburban and regional parks to meet demand. Rising rents, EU sustainability directives, and the changeable nature of the e-commerce space are also shaping the market landscape. The diverse occupier base and the need for flexible, modern facilities underscore the dynamic nature of the sector. Addressing these challenges and capitalising on opportunities will be crucial for stakeholders moving forward. Understanding the industrial and logistics market trends in Ireland unlocks new possibilities and enhances the operational processes in these sectors.

Market trends in the Irish Industrial & Logistics Sector
Structural Demand Drivers in Place
Undersupply of Modern Distribution and Warehousing Facilities
The Irish industrial and logistics market still faces a significant undersupply of modern distribution and warehousing facilities. Businesses are increasingly seeking advanced spaces to integrate technology and improve logistics operations. Existing infrastructure, often outdated, cannot meet these evolving needs. New EU directive on Embodied Carbon emissions requires all buildings to have zero emissions by 2050, which is also factored in for new leases on old stock. This undersupply is a critical structural driver that continues to shape the market dynamics. As a result, vacancy rates remain low at 2.4%, indicating intense demand and limited availability.
Slowdown in Dublin Construction Commencements
Adding to the supply constraints, new construction commencements in Dublin are slowing. The high demand and limited supply are keeping vacancy rates near historic lows, further intensifying the competition for available spaces.
Broad Mix of Occupier Types & Flexibility
The sector is characterised by a broad mix of occupier types, each requiring different levels of flexibility. From e-commerce giants to pharma and manufacturing firms, the demand for versatile and adaptable spaces is rising. Flexibility in facility use has become a key factor for tenants, accommodating a wide range of operational needs.
Rising Prime Rents in Dublin
Prime rents in Dublin rose by 13% in 2023, reaching €140 per square metre. The supply-demand imbalance in the market suggests that rents will continue to rise.
E-Commerce and Manufacturing Trends
While the e-commerce growth rate is slowing from its extremes of the pandemic era, the sector continues to be a significant driver of demand for logistics space. Stable manufacturing activities also contribute to steady demand. The manufacturing sector’s resilience provides a stable foundation for the industrial real estate market, balancing the fluctuations seen in e-commerce growth.
Corporate Governance and ESG
Corporate governance is increasingly driving sustainability credentials in the sector. The new Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) published by the EU on the 8th May 2024 requires all buildings, including those existing, to have zero emissions in both the construction and operational phases by 2050. These requirements will pose a challenge for the sector, as much of the stock will be considered outdated, requiring retrofitting to meet the new EU EPBD standards, significantly increasing capex required on older units.
On the imminent horizon however is the requirement for all new buildings to be zero-emission by 2030. To support this, the EU has adopted an ambitious package of measures to improve the flow of finance towards sustainable activities across the EU, which includes both the EU Taxonomy and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD).
Sustainability is, and will remain, at the forefront of considerations for developers, tenants and investors. From an Irish perspective, LEED Gold minimum certification is becoming standard for new buildings and facilities. Tenants are benefitting from enhanced building capabilities and modern logistics credentials, including reduced energy costs of up to 60%, future proofing their business against the incoming regulations, and achieving their Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) goals.
Sustainable buildings are also more attractive for onward investment, with lenders now requiring their own environmental criteria be fulfilled before funding or purchasing assets.
The medium and longer-term view is there are clear commercial and environmental benefits for those invested in sustainable buildings, and both the demand and rental income is more resilient as businesses prioritise eco-friendly spaces.
Incorporation of Sustainable Technologies
Modern logistics facilities are incorporating sustainable technologies such as glulam (glued laminated timber), low carbon concrete, solar PV (photovoltaic) panels, and EV (electric vehicle) charging stations. These features not only enhance the environmental performance of the buildings but also attract tenants who prioritise sustainability.
Tenant Requirements
Sustainability:
LEED Gold Certification and Sustainable Technologies
Tenants are increasingly demanding sustainable features in industrial and logistics facilities. LEED Gold certification is becoming a standard requirement, signifying a commitment to energy efficiency and environmental responsibility. In addition to LEED certification, tenants are looking for facilities equipped with solar PV panels, EV charging stations, and rainwater harvesting systems, helping buildings align with corporate sustainability goals.
Lower Carbon Alternatives
There is a growing preference for building materials and systems that reduce carbon footprints, such as glulam (glued laminated timber) structures and low carbon cladding panels. These materials help in minimizing environmental impact while providing durable and effective building solutions.
Key Physical Requirements:
Clear Height
Maximising rack height and storage density is a key driver in the design of distribution facilities. Higher clear heights allow tenants to make better use of vertical space, accommodating more inventory and improving operational efficiency.
Slab Design
The increasing use of robotic pickers and very narrow aisle (VNA) racking systems necessitates more stringent requirements for slab loading and flatness. Ensuring that slabs are designed to meet these requirements is crucial for attracting top-tier tenants who rely on advanced warehousing technologies.
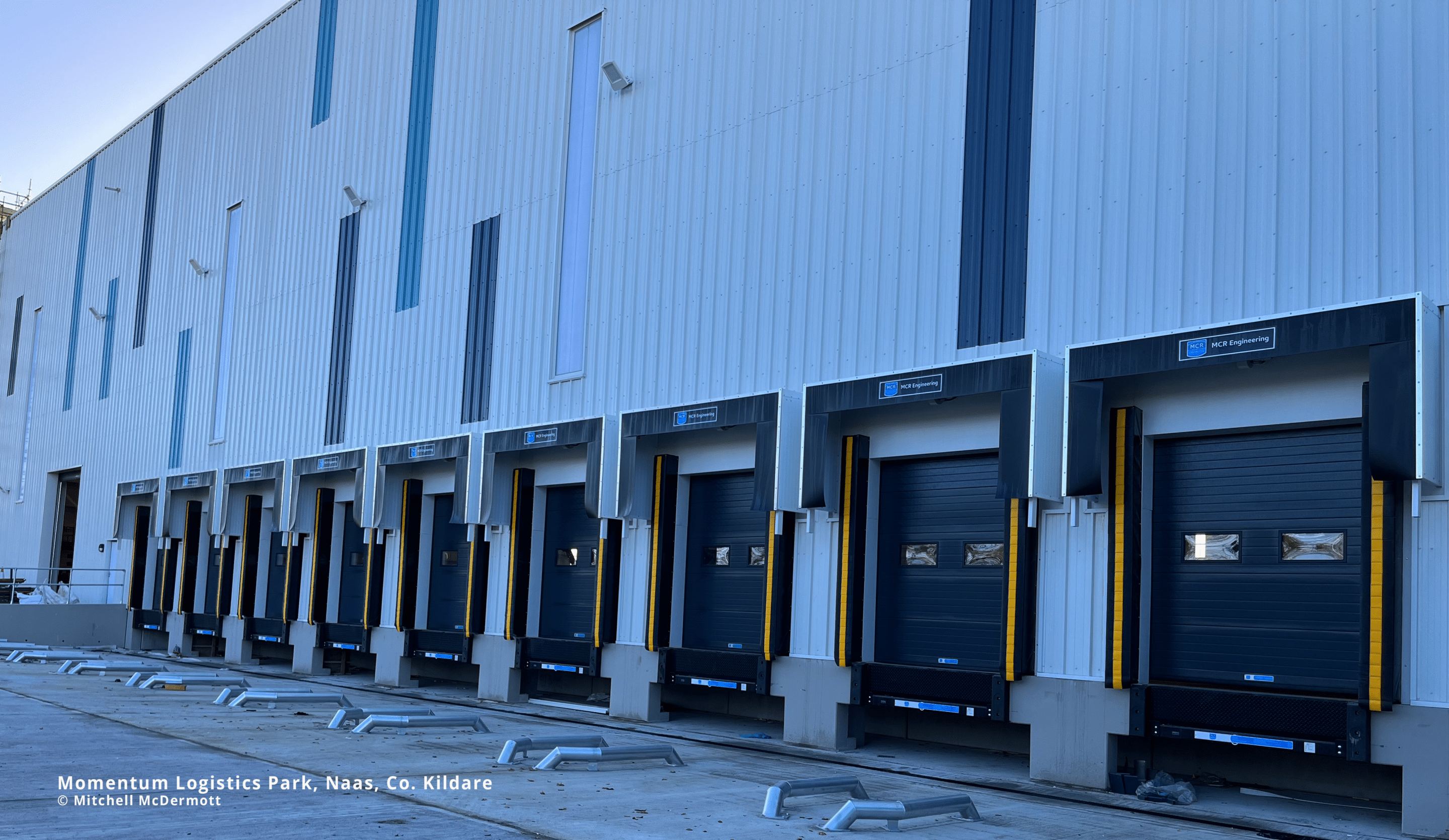
Yard Depth and Truck Access
Adequate yard depth is essential to accommodate a tenant’s truck fleet. This feature ensures that logistics operations can handle high volumes and large vehicle traffic efficiently. The potential to service future need for EV truck charging stations is also a consideration.
Future Availability of Power
As tenants move towards electrifying their vehicle fleets, the future availability of sufficient power is becoming a critical consideration. Facilities need to plan for increased electrical load capacities to support EV fleets and other energy-intensive manufacturing operations.
Modern Docking Equipment
State-of-the-art docking equipment is essential for efficient loading and unloading processes. Modern docks with advanced features can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce turnaround times for logistics providers.
Statutory Considerations in the Irish Market
Move Towards Sprinkler Systems
There is a growing trend towards Fire Officers making sprinkler systems a requirement in industrial and logistics facilities. Multiple code routes are available for compliance, and careful planning can help developers choose the most cost-effective option. It is crucial for developers and tenants to work closely with experts to navigate these requirements efficiently.
SUDs and Surface Water Attenuation Requirements
Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) are increasingly important in new developments to manage surface water runoff and prevent flooding. These systems include features such as permeable paving, green roofs, and retention basins. Adhering to these requirements is critical for gaining planning approval and ensuring that developments are sustainable and resilient to climate change impacts.
Connectivity and Placemaking
Planning officials want to see modern industrial and logistics developments that prioritise connectivity and placemaking to enhance the quality of life of staff and users and also reduce the ecological impact. Ensuring easy access to major transport corridors and public transport is therefore vital for efficient logistics operations and workforce convenience. Placemaking involves creating environments that are attractive and functional for employees. This can include integrating green spaces, recreational areas, and amenities that contribute to a higher quality of life for workers.
Ecology and Environmental Impact Assessment Reports (EIAR)
Environmental considerations are integral to the planning process. Developments that may have significant effects on the environment require an Environmental Impact Assessment Report (EIAR). Local authorities use EIARs to make informed decisions about planning applications, ensuring that ecological sustainability is factored into development approvals.
Concluding Remarks
The cyclical nature of the supply constraints in the market has led to a slowdown in construction commencements in Ireland in 2024, which has resulted in increased competition for available spaces. EU directives to achieve Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2030 and 2050 will drive demand for modern, purpose-built facilities or retrofitted units. Location, size and specification are still the main cost drivers, with the impact of new fire regulations and the trend towards more efficient buildings apparent in the average cost to complete units. We anticipate further demand in the market in 2025 fuelled by falling interest rates and continued growth in the Irish economy, along with ever-evolving sustainability and technology requirements.
Authors:
Alex Moore Senior Project Manager
Lisa Cleary Associate
Ronan Tynan Director & Head of Project Management
Professional advice should be sought for specific projects. Costs are for construction only and exclude the following VAT, Tender Inflation from January 2024, Site Acquisition, Planning and Statutory Fees, Development Contributions, Capital Contributions for Services connections, Bonds, Professional Fees, Sales and Letting Costs, Marketing, Legals, Valuers, Accountancy Costs, Finance Costs, Owner Insurances, Adjoining Neighbour Costs, Abnormal Ground Conditions, External Works. Sources: Colliers, CBRE, JLL, Savills, The European Commission.